The Richest Countries In The World Might Surprise You
It might surprise you that the United States is not the richest country in the world, at least not in terms of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita. That value is used to determine all of a country's wealth divided by its population. Let's take a look at the countries with the highest GCP in the world.
The United Kingdom — GDP per capita: $45,491

The United Kingdom has a GDP of $45,491 per capita. The UK has been experiencing a wealth boom for the past few decades.
The South East is the wealthiest region of the UK, while the North East is the poorest.
France — GDP per capita: $45,586

France has a GDP of $45,586 per capita. The biggest industries in France are energy, manufacturing and technology, transportation, agriculture, and tourism.
In January 2019, France increased its minimum wage to €10.03 per hour, which is $11.24 U.S. dollars per hour.
Canada — GDP per capita: $48,604

Canada has a per capita GDP of $48,604. Close to 70% of Canada's GDP comes from the service industry.
Canada is also a leader in energy production and exports. Secondary industries include manufacturing, agriculture, mining, and fishing
Belgium — GDP per capita: $49,095

Belgium has a per capita GDP of $49,095. The land between Antwerp and Brussels has become a major zone for manufacturing.
Belgium's economy is largely reliant on international trade. 3M, Coca-Cola, and ExxonMobil all manufacture products in Belgium and then export them around the world.
Hong Kong — GDP per capita: $50,216

Hong Kong is an autonomous territory in China with a GDP per capita of $50,216. Financial services, tourism, trading, and logistics are the key industries that have contributed to its economic growth.
Hong Kong hasn't caught up to America yet, but at this rate, they just might.
Germany — GDP per capita: $51,642

Germany has a per capita GDP of $51,642. The machinery, automotive, and aviation industry is by far the largest industry in the country.
Close behind is the chemical and medical industry, the consumer and service industries, and the energy and environmental technology industry.
Finland — GDP per capita: $52,320

Finland is coming in strong at number 14 on this list. It has a per capita GDP of $52,320. Finland's largest industry is the electronics industry which makes up around 21 percent of the country's economy. Machinery, vehicles and other engineered metal products also make up around 21 percent, and the firest industry makes up around 13 percent.
Finland doesn't need to rely on other countries for natural resources like timber, minerals, and fresh water.
Austria — GDP per capita: $54,606

Austria rings in at number 13 on the list of the top 20 richest countries with a per capita GDP of $54,606. While Austria exports a lot of goods and products, mostly machinery, metallurgical products, and textiles, its main industry is tourism.
Austria is well known for its castles, historical buildings, and palaces. People come from all over the world to see this country's architecture and landscapes. This country has a well-developed economy and a high standard of living.
The Netherlands — GDP per capita: $56,415

The Netherlands sits at number 12 on this list with a per capita GDP of $56,415. This country is one of the top ten exporters in the world. Mostly, The Netherlands exports food. Its foodstuffs industry is the biggest industry in the country.
Other major industries include energy, chemical, trade, machinery, metallurgy, electrical goods and services, and tourism. Minimum wage is dependant on age in The Netherlands, but for those over 22 years old the minimum wage is €1,615.80 per moth.
Sweden — GDP per capita: $57,945
Sweden comes in at number 11 on this list with a per capita GDP of $57,945. Sweden is a major world exporter of timber and other forest products. This country also has a large iron and steel industry. Its economy is heavily reliant upon foreign trade.
Because Sweden remained neutral during World War II, its infrastructure wasn't damaged by the war and it didn't have to spend resources rebuilding its cities and bank systems. That's a major reason why Sweden is better off economically than most other European countries.
Australia — GDP per capita: $58,820

Australia just squeaks into the list of the top 10 richest countries in the world with a per capita GDP of $58,820. The largest industry in Australia is the service industry wich comprised over 70 percent of the GDP. Tourism is also a large part of Australia's economy.
Less substantial but still significant industries in the region include healthcare, media and entertainment, finance, mining, agriculture, and manufacturing. The minimum hourly wage in Australia is $18.93, which is just over 13 American dollars.
Singapore — GDP per capita: $62,690

Singapore comes in at number 9 on this list with a per capita GDP of $62,690. Singapore's biggest industry is its manufacturing sector which accounts for 20-25 percent of the country's GDP. The manufacturing sector is involved in manufacturing electronics, health care equipment, chemicals, and transport engineering.
Singapore doesn't have access to a lot of natural resources, so a lot of the revenue from the manufacturing sector goes towards importing natural resources for raw goods.
Denmark — GDP per capita: $63,434

Denmark comes in at number 8 on the list of the top 20 richest countries with a per capita GDP of $63,434. Agriculture is a huge industry in Denmark. Over 60 percent of the total area of the country is used for agricultural purposes. Tourism is also an important industry in Denmark; it brings in around 125 billion dollars of revenue per year.
Secondary industries include energy and transportation. There is no official minimum wage in Denmark, although the typical lower-end wage tends to hover around 16.60 U.S. dollars per hour.
The United States Of America —GDP per capita: $64,906

Here we are, my fellow Americans, sitting comfortably at number 7 on this list. Our per capita GDP is $64,906. The largest industry in America is the health industry. That's why you're constantly being bombarded with ads for new controlled substances (with long lists of side effects).
America also has strong financial services, consumer products, logistics, transportation, business, real estate, and construction industries. America is doing pretty well economically, but we're not quite at the top of the list.
Qatar — GDP per capita: $65,062

Qatar sits at number 6 on this list with a per capita GDP of $65,062. The largest industry in Qatar is natural gas. The country sits on a lot of crude oil and natural gas, which is a huge contributor to the nation's economic success.
Qatar also relies on its steel industry, its financial industry, it's fertilizer industry, and commercial ship repair. The 2022 World Cup is set to happen in Qatar, which will boost the country's economy even more.
Iceland — GDP per capita: $78,181

Iceland is the 5th wealthiest country in the world with a per capita GDP of $78,181. Major industries in Iceland include tourism, fish processing, aluminum smelting, ferrosilicon production, geothermal power, and hydropower.
The average salary in Iceland is slightly higher than the minimum wage in the country. The average monthly wage is around 410,000 ISK net or 3238.06 U.S. dollars. The minimum monthly wage is equivalent to 2400 U.S. dollars. Iceland is starting to sound like a pretty great place to live.
Ireland — GDP per capita: $81,477

Ireland comes in at number 4 on this list with a per capita GDP of $81,477. We all know about the way leprechauns get their gold, but Ireland gets its wealth from the land. Ireland's thriving economy is largely due to the country's rich natural resources as well as its agriculture, mining, forest, and fishing industries.
This country also has a strong pharmaceutical industry, as well as strong software, financial, and trade industries. Chalk it all up to the luck of the Irish.
Switzerland — GDP per capita: $83,832

Alright, now we're getting into the top 3. Switzerland has a per capita GDP of $83,832. Switzerland has a varied economy, which is probably why this country is so economically prosperous. It's strongest industries and exports include machinery, chemicals, watches, textiles, precision instruments, tourism, banking, and insurance.
Switzerland has no official minimum wage. Wages are determined by private corporations, but minimum monthly wages for unskilled laborers are around 2,200 to 4,200 francs. Swiss francs are very similar in value to U.S. dollars.
Norway — GDP per capita: $86,362

Norway is the second richest country in the world with a per capita GDP of $86,362. Norway's petroleum industry is essential for the country's economy. Oil and gas literally and figuratively fuel this place. Hydropower is also a huge industry in Norway.
Norway is also known for aquaculture, shipping, and tourism. Nordic countries such as Norway and Sweden don't typically have an official minimum wage, but the average minimum salary in Norway is around 170 NOK per hour, or 21 U.S. dollars per hour.
Luxembourg — GDP per capita: $119,719

We've made it to the very top of the list. Luxembourg is the richest country in the world with a per capita GDP of $119,719. Luxembourg has a huge financial sector which makes up around 36 percent of the GDP. Steel, telecommunications, and tourism industries combined make up around 13 percent and agriculture accounts for less than one percent.
The minimum wage in Luxembourg is 2,071.10 EUR per month as of January 2019. That's 2321.21 U.S. dollars.
Japan — GDP per capita: $45,565

While Luxembourg is the richest country in the world, there are plenty of other countries that are working their way up to the top. Take Japan for example. Their per capita GDP as of 2019 is $45,565. While that number is nominal compared to Luxembourg, Japan is the world's second-largest developed economy.
Just over 68-percent of their GDP comes from services, likely dominated by the country's tourism. A little over 30-percent comes from industry, as Japan is a dominant manufacturer of electronic goods and automobiles.
United Arab Emirates — GDP per capita: $69,381

The United Arab Emirates has the second-largest economy in the Middle East. Their GDP per capita is $69,381 which has only been growing after the Emirates have successfully diversified their economy.
A majority of their economy, of course, relies on oil revenue, particularly petroleum and natural gas that accounts for more than 75-percent of their economy. Another large factor of their economy is tourism, as their construction boom has made the UAE home to some of the world's most luxurious hotels.
Italy — GDP per capita $39,636

The third-largest national economy in the monetary union of the European Union belongs to Italy, whose GDP per capita caps in at $39,636. Their economy relies heavily on its exports, which include machinery, vehicles, pharmaceuticals, furniture, food, clothing, and robots. Because of this, Italy ranked as the eighth-largest exporter in the world after they exported $514 billion in 2016.
The average salary per month in Italy is €2,595, which converts to about $2,916. Many of these jobs are in industry or services.
Bahrain — GDP per capita: $26,083

Bahrain has a population of $1.5 million combined with a meager unemployment rate. Surprisingly, fewer than one percent of the labor force in this country is unemployed, which ranks it among the best on this list.
Bahrain is another country that relies on its natural resources. In 2017, 38% of its exports came from refined petroleum, which is their main export. Iron ore and aluminum made up 5.6% of their total exports in 2017 as well.
South Korea — GDP per capita $41,350

South Korea has the 11th largest economy in the world, with a GDP per capita of $41,350 in 2018. South Korea's economy stands out internationally as it is known for its incredible rise from one of the world's poorest countries to a developed, high-income country within a few generations.
Automobiles, mining, construction, armaments, and tourism make up the dominant sectors of South Korea's economy. More than 27 million South Koreans work in these industries which keeps the country's unemployment rate at a low 3.7 percent.
Slovenia — GDP per capita: $26,758.90
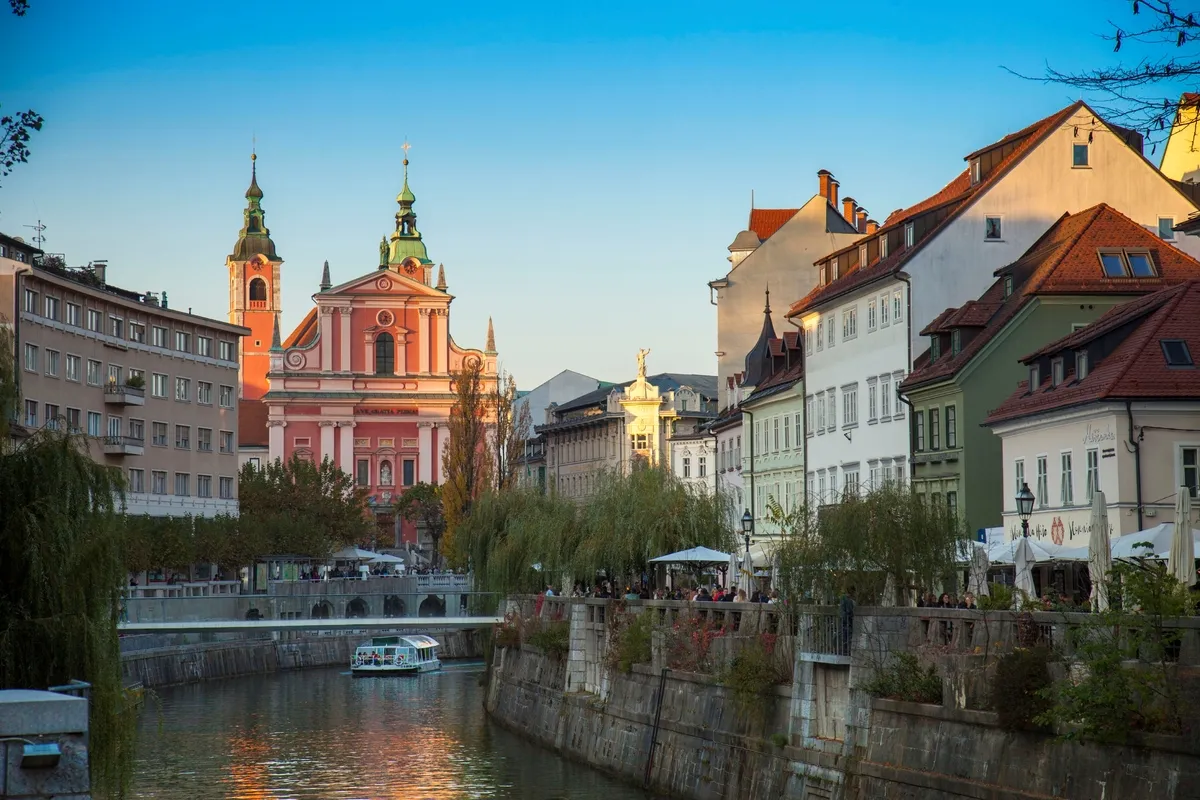

Slovenia is a well-developed country where the citizens enjoy stability and a high level of prosperity. The people in their workforce have a high level of education as well. With a well-built infrastructure, the economy of Slovenia thrives thanks to where they're located as well (major transport crossroad).
The economy suffered starting in the late 2000s thanks to the European economic crisis. But after 2013, things started rising again and saw two-thirds of the working population getting employed.
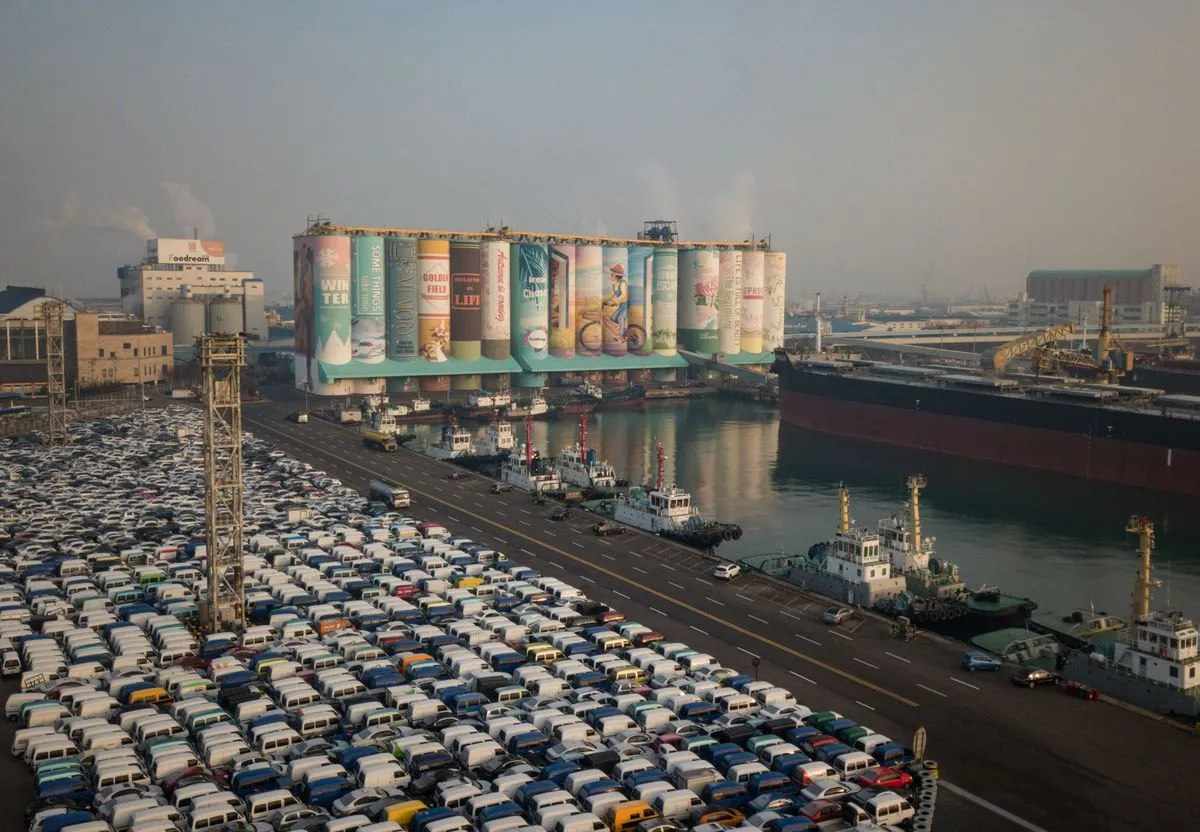
Taiwan — GDP per capita: $26,309

Taiwan is the 7th largest economy in Asia. Starting in 2018, financial services, utility services, and telecommunication became the three highest individuals paid sectors in Taiwan. The current minimum wage in Taiwan is NT$23,000, or USD 740.77 per month.
That minimum wage is the lowest monthly wage that employers can legally pay their hard-working employees. The exported goods from this country vary a lot, but the main items are steel, electronics, ships, and wireless communication equipment.
Czech Republic —GDP per capita: $37,370
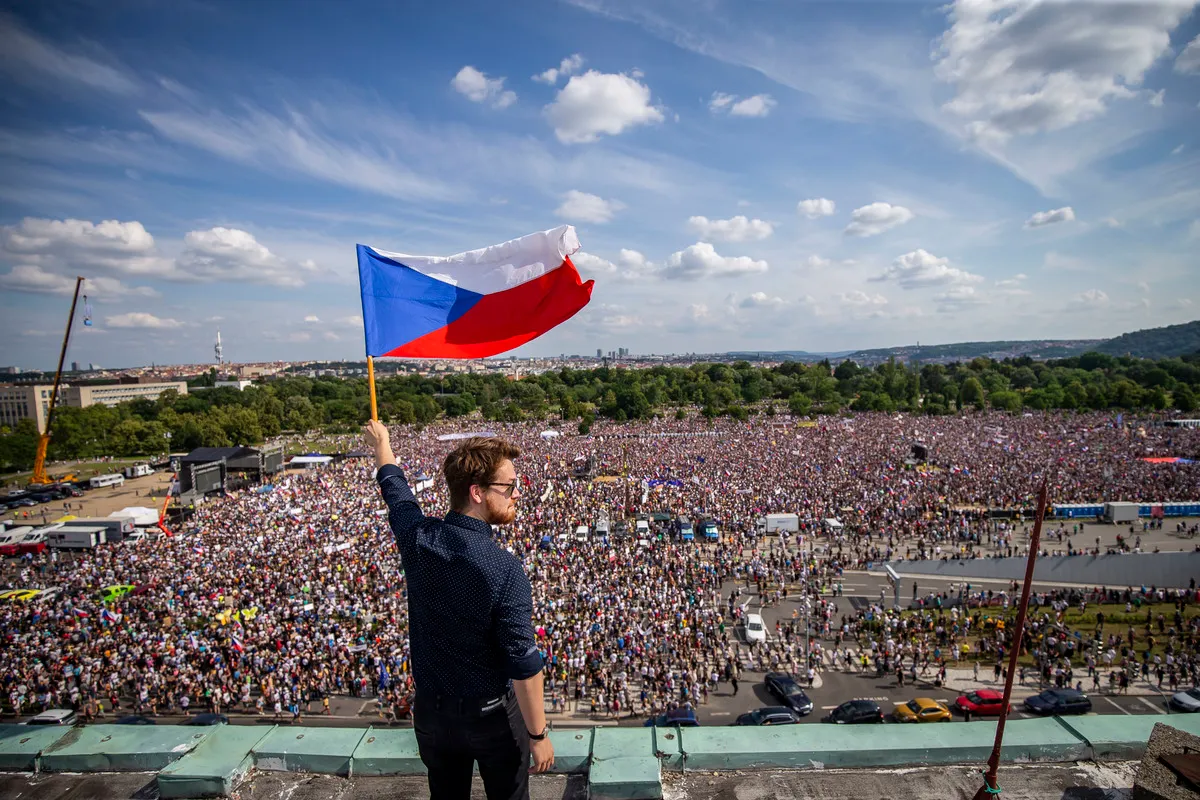

The Czech Republic has figured out how to run its economy smoothly. They came up with an export-oriented social market economy that thrives on services, innovation, and maintaining a high-income welfare state. They're no slouches when it comes to their economy.
They may be a part of the European Union, but they use their own currency, the Czech koruna, rather than the Euro. As of May 2019, the Czech Republic earned the lowest unemployment rate of all countries in the European Union at 2.2%.
Portugal — GDP per capita: $23,176

When it comes to international trade, the majority of it goes through the European Union. Of the countries involved in trade, they receive 72.8% of Portuguese exports. The economy of this country continues to rise and expand since the third quarter of 2014.
They have had a yearly GDP growth of 1.5% since the second quarter of 2015. The unemployment rate is at 6.7% as of quarter three of 2018, and the average net salary is 10,284 Euros or $11,659.
Spain — GDP per captia: $40,138

Spain has the fifth-largest economy in Europe and has a GDP per capita of $40,138 in 2018. This has increased significantly since Spain's financial crisis of 2007 to 2008. The crisis plunged the country into a recession that left a quarter of the Spanish workforce unemployed by 2012.
But in 2015, their GDP increased by 3.2 percent after having recovered 85-percent of its lost GDP since the recession. Spain is working to recover its unemployment rates in its main industries such as machinery, pharmaceuticals, shipbuilding, automobiles, metals, and chemicals.
Puerto Rico — GDP per capita: $39,737

According to the World Economic Forum, Puerto Rico has the most competitive economy in Latin America. With a GDP per capita of $39,737, Puerto Rico's economy is driven by manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, textiles, petrochemicals, and electronics. Another large factor in their economy is the service industry which is comprised of finance, insurance, real estate, and tourism.
Despite its competitive economy, Puerto Rico has been experiencing an economic depression on a macroeconomic level. It doesn't help that there is a lack of natural resources due to the country's size as an island, making it heavily reliant on imports.
Malta — GDP per capita: $29,200

Malta sits at the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, right in the crossroads of Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East, which is ideal for its open-market economy. As a result, they're heavily reliant on foreign trade, electronics manufacturing, tourism, and financial services.
Malta's GDP per capita is $29,200 thanks to its productive labor force, yet poverty remains one of the country's most prominent social issues. In 2014, they addressed this by employing six branches of social services in health, environment, culture, income, and education.
Estonia — GDP per capita: $35,095

Heavily influenced by the developments in the Finnish and Swedish economies, the Estonian economy is highly advanced. As part of the European Union, Estonia sees an unemployment rate of 5.4% with an average net salary of 1,193 Euros ($1,340).
The main exports from the country are wood and articles made of wood, electrical equipment, mineral products, and agricultural products. Before WWII, they based their economy on agriculture. Once they detached themselves from Communism and became a market economy, Estonian became a pioneer in the global ranks.
Saudi Arabia — GDP per capita: $56,337

Saudi Arabia is a top economy in the world, but it's dependent on oil thanks to having the second-largest petroleum reserves. They are, however, the largest exporter of petroleum. Saudi Arabia sits on a total worth of $34.4 trillion and has the second most important natural resources in the world.
Knowing that they depend on oil so much, the country launched the Saudi Vision 2030 in 2016. Saudi Vision aims to lessen the country's dependence on oil and switch things up.
Slovakia — GDP per capita $35,129

From 2000 to 2008, Slovakia saw a jump of 10.4% in their GDP. That isn't something that happens all the time, so they earned the nickname of the Tatra Tiger. The economy of this country is based on them becoming an EU member in 2004 and using the euro starting in 2009.
As of quarter one of 2018, their unemployment rate was 5.72%. Their service sector grew exponentially in the last ten years, and the service sector now hosts jobs for 69% of the population.
Brunei — GDP per capita $51,600

The Sultan of Brunei is often considered the wealthiest man in the world, so it makes sense that the small country has a wealthy economy. With a GDP per capita of $51,600, Brunei's economy is almost entirely supported by exports of crude oil and petroleum. Brunei is the third-largest oil producer in Southeast Asia, producing around 180,000 barrels per day.
Their high GDP is also supported by income from overseas investment supplements. Foreigners make up a significant portion of the workforce, though Brunei officials try to regulate the amount of immigration of foreign labor so as not to disrupt their society.
Cyprus — GDP per capita: $38,048

The Middle Eastern country of Cyprus adopted the Euro and became a part of the Eurozone in 2008. Many offshore businesses turn to Cyprus for the country's low tax rates, while tourism, shipping, and financial services serve to boost its economy.
Unemployment in Cyprus in recent years has been around 6.5 percent, while the average salary per month is around €1,827, which converts to a little over $2,000. The largest sector in Cyrpus is services which account for 86.8 percent of the GDP.
Kuwait — GDP per capita: $29,040

Kuwait's economy is largely reliant on its petroleum industry and has around 94 billion barrels of recoverable oil reserves. They produce an estimated 2.5 million barrels per day and those numbers are only going up, which helps make its GDP per capita $29,040.
Outside of oil, Kuwait's economy also relies on financial services as many of their firms account for over a third of the country's assets. Financial and banking companies comprise more than half of the market capitalization.
Greece — GDP per capita: $27,812

Starting in 2018, Greece became the 17th largest economy out of the 28 members in the European Union. 80% of the countries economy comes from service, while industrial sectors comprise 16%. The agricultural industry totals a small 4%.
The scary part about Greece is that their unemployment rate is a bit higher than most on this list. As of April 2019, it was at 17.9%. Their most significant export is petroleum oils, aluminum, and electronic equipment.
Lithuania — GDP per capita $34,825

No surprise here that Lithuania would creep into this list, as it belongs to the group of high human development countries. Being the first country to gain independence from the Soviet Union in 1990, it quickly became a market economy.
Lithuania's economy grew over 500% after gaining independence. That's huge. Their unemployment rate is at 6.3% as of quarter three of 2018, which isn't the worst, but it could improve. 21.9% of their people live below the poverty line, too.









