Vitamins and Minerals to Avoid While Pregnant
Vitamins are a good thing, right? Not always! When you are pregnant, avoid taking too much of these vitamins and minerals as they can have bad affects on your baby's health.
Vitamin A

Vitamin A will help your baby's respiratory system, circulatory system, nervous system, eyes, bones, and organs develop. The prenatal vitamin will have Vitamin A in it, so it is important not to take anymore than your prenatal vitamin as it can have adverse affects on your child. Just what are these effects?
Effects of Vitamin A
Taking more than 10,000 international units a day of Vitamin A can cause birth defects to your unborn child. Taking any more Vitamin A supplements than what is already in your prenatal vitamins can be bad. Don't worry about getting too much Vitamin A from fruits and vegetables because the body only uses the vitamin from the food if you need it, so it won't cause symptoms if you eat too much. But what if your unborn child does not get enough vitamin A?
Inadequate Vitamin A
While you are pregnant and do not get enough vitamin A, your baby could be born preterm. Furthermore, they may not have enough liver stores of vitamins and their retinol concentrations in the plasma may stay low throughout their first year of life. Vitamin A deficiency in preterm babies has been linked to gastrointestinal diseases, chronic lung diseases, and eye problems.
Vitamin E

Vitamin E has been shown to help stop complications in pregnancy, such as preeclampsia. There have been conflicting reports about this and how much good and harm Vitamin E actually does. In 2005, a study published in Reproductive Toxicology showed that Vitamin E doesn't cause birth defects. The study went on to say that at high doses it may cause low birth weight. A more recent study came out that had a different opinion.
October 2012

The study that came out in October 2012 in the European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology suggested that taking Vitamin E as a supplement along with the prenatal vitamin could actually have adverse effects. One of these defects is a heart defect, which could complications for the rest of your child's life.
Another Vitamin E Study

There was another study by researchers at Erasmus MC University Medical Center in Rotterdam that found women who took more than 14.9 milligrams during the first two months of pregnancy were nine times more likely to have a child with a heart defect. That is a big jump so it is best to stay on the side of caution and do not take a vitamin E supplement unless specified by your doctor.
Vitamin B6

Vitamin B6 is good for your developing child's nervous system and brain. It helps these areas develop properly while your child is in the womb. Most prenatal vitamins contain about 1.9 milligrams or 100 percent of the daily value when it comes to vitamin B6. It can even help you by relieving nausea and vomiting from the pregnancy. So just what can large amounts of B6 do to your developing baby?
Birth Defects

Taking too much B6, especially in the first trimester, can actually cause physical damage to your baby's body, and nerve damage as well. The physical defects can happens to the arms and legs, causing them not to develop properly. Another side effect of too much vitamin B6 is the unborn child can become addicted to it. Once they are born, they will have withdrawal symptoms, which can be detrimental to their health.
How Much B6?

While you are pregnant, the recommended amount of B6 is 1.9 milligrams a day. Once you start breastfeeding, that should increase slightly to 2.0 milligrams a day. It is not super strict because if you do not get enough of the vitamin one day you can make it up the next day. Just watch out for supplements that have high doses, such as 100 milligrams or more.
Folic Acid
Folic acid is supposed to protect your baby from birth defects in the brain and spinal cord. Yet, too much folate, such as vitamin B9 and B12 can actually cause harm to your child. There is new research coming out warning pregnant mothers against taking too much folate. You should still take your prenatal vitamins, but avoid adding a folate supplement, otherwise your child may be at risk for Autism.
Autism

Researchers are discovering more information about the link between folate and Autism when it comes to pregnant women. Folate is found in fruits and vegetables, as well as folic acid supplements. The study showed women who had high levels of folate in their blood were more likely to have a child with Autism when compared to mothers who had normal folate levels. But what happens if you do not get enough folic acid?
Folic Acid Deficiency

Too much folic acid can harm your child, but not getting enough can also harm the developing baby as well. Women who are pregnant and do not get enough folic acid may get anemia and low levels of white blood cells and platelets. Furthermore, not enough folic acid can cause neural tube defects, which are defects to the spine and spinal membrane.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for a healthy pregnancy, but too much can hurt your child. Vitamin D regulates the phosphate and calcium in your body, which keeps your muscles, teeth, and bones healthy. Women who are breastfeeding need 10mcg of Vitamin D a day, so check your prenatal vitamin for the amount of vitamin D that is in it. Taking additional vitamin D can cause harm to your developing child.
Vitamin D Toxicity

Too much vitamin D while you are pregnant can cause problems with the developing fetus' heart. The heart valves may not form properly or if you take really large quantities, the vitamin D toxicity may lead to miscarriage. If you are deficient in vitamin D before you are pregnant, make sure to talk to your doctor about the proper dose for your and your developing baby for a healthy pregnancy, because a vitamin D deficiency can be detrimental as well.
Vitamin D Deficiency

While you are pregnant, not getting enough vitamin D can cause a lot of issues for you and your child. You could develop preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and need a c-section. For the baby, they are susceptible to low birth weight, hypocalcemia, neonatal rickets, asthma, and diabetes. Talk to your doctor about how much vitamin D is right for you.
Iron

Iron is a good supplement to take if you are anemic, as it can help this problem. A doctor may prescribe iron as a supplement to your prenatal vitamin if you are anemic, however; if you take it on your own without a doctor's recommendation you may be getting too much which can cause problems with your pregnancy. Iron is a double edged sword as too little early in your pregnancy can cause low birth weight and premature birth. Yet, too much can cause other problems.
Issues with Iron

Too much iron in a pregnant women's system can actually cause low birth weight and premature birth weight as well. Therefore, taking too much or too little iron can actually cause the same problems. Research in animals showed that too much iron can increase the risk for cancer as the excess iron can trigger the formation of free radicals. Iron is a tricky supplement so you should be monitored by your doctor if you need more or less of it during your pregnancy.
Iron Deficiency

Some pregnant women are more at risk for an iron deficiency than other. If you are pregnant with more than one baby, have two pregnancies close together, horrible morning sickness, are a teenager, or have a history of anemia you are more likely to get it while you are pregnant. If you have low iron while you are pregnant, you how a higher risk for a low birth weight baby, blood transfusion, postpartum depression, a baby with anemia, or a baby with developmental delays.
Magnesium

Magnesium is recommended for pregnant women and the dose is 350 milligrams per day. That amount is the largest that is considered safe to be tolerated. Magnesium is important because it helps your organs and muscles. It also helps keep away leg cramps while you are pregnant. Yet, like any mineral, too much can actually do more harm than good. So just what does too much magnesium cause?
Too Much Magnesium
Magnesium interferes with calcium absorption, so taking too much magnesium can actually cause your calcium to become depleted. This can be fixed by having an infusion of calcium, which could be up to three to five days in the hospital. In addition, not enough calcium and too much magnesium can increase the risk for rickets and cause your child to have chronically low calcium levels. There is a small chance of respiratory distress as well after they are born. What happens if you don't get enough magnesium?
Magnesium Deficiency

Not getting enough magnesium while you are pregnant can increase your chance of miscarriage. It has also been shown to play a role in neonatal hypocalcemia in newborns who mothers were diabetic and fetal malformations as well. In animals, magnesium deficiency showed an increase in edema and periventricular bleeding in newborn pups. So it is important to get enough magnesium, but not too much.
Sugar

While sugar is not technically a vitamin or mineral, it is something we eat every day in our diets and can cause birth defects or cause problems once the child is born. If a woman eats too much sugar while she is pregnant, is overweight and becomes pregnant, or becomes diabetic while she is pregnant, her baby is at higher risk for issues. So just what are these issues?
Sugar Babies

If you eat too much sugar while you are pregnant, your baby may experience withdrawal symptoms once they are born. These can get so bad some babies end up on sugar drips right after they are born to combat these symptoms. Furthermore, these babies who were exposed to lots of sugar while in the womb continued to make too much insulin after they are born. Yet, you want to make sure you get enough sugar as well.
The Right Amount of Sugar

You should eat 300 more calories than you normally do while you are pregnant to compensate for your growing baby. If you do not eat enough, your blood sugar may drop causing hypoglycemia. If you have hypoglycemia, then your baby has a higher chance of being admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit.
Calcium

Calcium is important for your health as well as the baby's health. Not only does it help with the development of bones, but it also prevents pre-term labor and high blood pressure while you are pregnant. So it is good to have a healthy diet that consists of calcium to prevent these and keep you and your baby on track. Yet, taking a calcium supplement can be detrimental to your health if you get too much.
Kidney Stones

Too much calcium while carry a baby can actually put you at risk for kidney stones. It can also lead to excess calcium in the placenta and in your unborn child. Stay away from calcium supplements while you are pregnant unless your doctor specifically prescribes them for you. Instead, eat a healthy diet of green leafy vegetables, almonds, soy milk, and sesame seeds. Not getting enough calcium can be detrimental to your body while you are pregnant.
Calcium Deficiency

Not enough calcium while you are pregnant can cause the fetus to draw on calcium from your body. This ensures your child will get enough calcium, but can cause complications for you as you get older. Try to get 1,300 milligrams of calcium a day while you are pregnant. Avoid taking in more than 2,500 milligrams of calcium as this can cause the issues stated above.
Biotin
Biotin is essential in our diets because it prevents hair loss, depression, hallucinations, tingling, numbness, and facial rashes. We get a lot of biotin through what we eat each day, but studies have shown some pregnant women are deficient in biotin. This can cause issues for the developing fetus.
Biotin Issues

If you are pregnant and do not take enough biotin, there may be a risk your child could develop birth defects in the womb. A study published by the Journal of Nutrition showed that a biotin deficiency n animals was linked to cleft lip, cleft palate, and other skeletal deformities. Yet, extensive research has not been done on too much biotin, so it is important to talk to your doctor about the supplements you are taking.
Choline

Choline is another nutrient that we need in our bodies so we can grow properly. Choline is important for our cells to grow and function at their optimal level. McGill University and Cornell University recently put out a study that showed what happens when mice become deficient in choline while they are pregnant. So what did that study show?
Choline Defects

The study showed that the mice who were deficient in choline had a higher number of babies that had heart defects. It is also important for liver metabolism and healthy nerve functioning. Pregnant women need 450 mg of choline a day. This does not mean you need a supplement because choline is found in bananas, spinach, eggs, bacon, cauliflower, and soybeans.
Fluoride
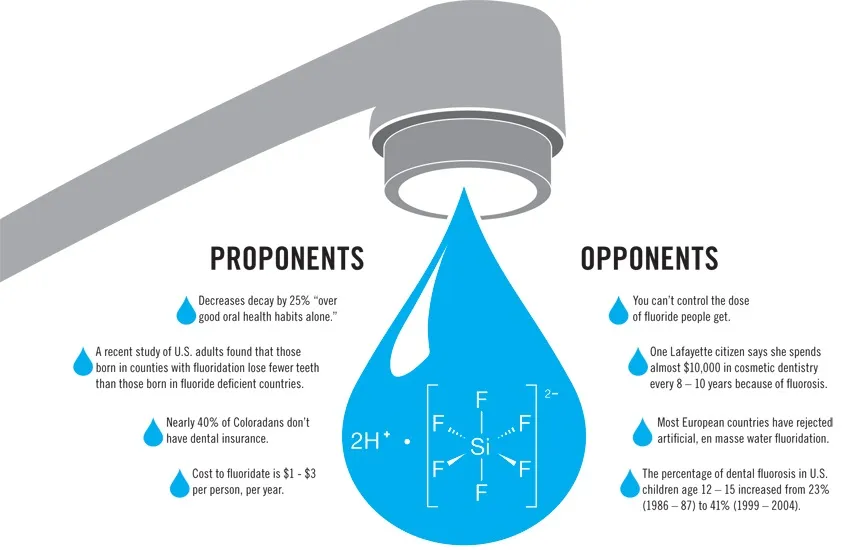
Fluoride is put into our water and over 75 percent of America's water system is fluoridated. The amount is about 1 part per million and about half of this accumulate in your body over time. Chronic exposure can have negative effects on your body as well as your baby's body. Before you are pregnant, fluoride can suppress your thyroid and interfere with your immune system. The list goes on.
Bad Effects of Fluoride

Another bad effect of fluoride before you even get pregnant is how it can effect your fertility, which is negatively. Male rates were exposed to fluoride in their drinking water and their sperm counts went down. While you are pregnant, research has shown a correlation between fluoride exposure and low IQs as well as psychiatric disorders. Just something to keep in mind before you take your next sip of tap water. Check out these studies on fluoride.
Studies on Fluoride

The Yu/Dong Study investigated 20 fetuses, 10 from a low-fluoride area and 10 from a high-fluoride area, to see the impact of fluoride. The study found those with high-fluoride had lower levels of norepinephrine and higher levels of epinephrine. Norepinephrine plays a rose in response, emotions, and other important activities. When these levels drop, the central nervous system may be weakened. The Du Study found that fluorine crosses the placenta and accumulates in the brain and impacts the central nervous system and stunts neuron growth.
Iodine

Iodine is an essential part of our thyroid hormones, which take part in our metabolism and neurological development. If you do not get enough iodine before you get pregnant, this can lead to hypothyroidism, which has many health problems with it depending on how deficient you are in the mineral. Yet, it get worse if you are pregnant and deficient in iodine.
Iodine Deficiency

Iodine deficiency while you are pregnant can cause fetal hypothyroidism. Beyond this, a deficiency can cause neurological defects, preterm birth, and even miscarriages. Pregnant women should get 220 micrograms a day and breast feeding women should get 290 micrograms a day of iodine. Good foods to eat include poultry, eggs, grains, and dairy products to ensure your iodine is on track. What happens if you do get enough iodine?
Importance of Iodine

Iodine is a good mineral to have in your diet especially while you are pregnant because it can increase your child's IQ. A 2013 study showed that women who did not get enough iodine while they were pregnant had children whose IQ were on average three points lower by the time they were eight years old. By age nine, they were not able t read as well.
Niacin

Niacin is another essential nutrient to our body. Supplements are normally used to treat high cholesterol. If you are deficient in niacin, you may experience tiredness, headaches, anemia, mouth lesions, skin lesions, and nausea. Does not sound like fun. Yet, when you become pregnant and if you get too much niacin, it can become a problem.
Niacin Problems

If you become pregnant and are taking niacin supplements, you will need to talk to your doctor about whether you should continue these supplements. In lab animals, niacin has been associated with birth defects so it may harm the developing child in pregnant women. Furthermore, a recent study showed that women who were deficient in niacin had a higher risk of their child developing spina bifida. A healthy diet is vital to ensure you are getting enough nutrients without having to take supplements. Severe problems can happen if you do not get enough niacin.
Not Enough Niacin

A few symptoms that you are not getting enough niacin include: indigestion, fatigue, canker sores, vomiting, and depression. If you have a severe deficiency, you may experience a bright red tongue, headache, rash on skin, fatigue, disorientation, and memory loss. This can happen whether you are pregnant or not, so make sure to eat a healthy diet.









